How Conventional Batteries Leave the Factory
Yuasa Conventional batteries leaves the factory as Bottle Supplied (BS):
- Bottle Supplied (BS) – dry Conventional batteries are shipped with the electrolyte stored in a plastic container. The battery is filled with electrolyte from the container when it’s ready to be activated. Conventional batteries have a shelf life of 2 years from the manufacturer as long as they remain sealed. Proper seal for Conventional batteries means filler caps and a red vent caps are installed and stored at room temperature. Once a battery is unsealed, it should be activated, charged, and installed. The cell plates of an unsealed, uncharged battery will begin to oxidize, making it more difficult to charge later.
The Process to Activate a Conventional Battery
- The battery must be out of the vehicle and placed on a level surface. Remove the filling caps (red, yellow, or green colored battery caps).
- Remove the red sealing cap from the vent elbow. If the battery has a red cap on the vent elbow, remove it and throw it away. Never put this cap back on the battery after it is filled with acid as the buildup of internal gas pressure can cause the battery case to rupture.

- Using the acid bottle supplied with the battery, place the container upright on a flat surface. Carefully cut off the tip of the bottle’s spout and attach the short tube provided. Caution: Do not squeeze the bottle when cutting the fill tip. Do not smoke when activating a battery or handling battery acid. Always wear plastic gloves and protective eye wear.
- Fill the battery with the electrolyte supplied with the battery. Do not use water or any other liquid to activate a battery. Electrolyte should be between 60 and 86 degrees Fahrenheit before filling. If electrolyte is stored in a cold area, it should be warmed to room temperature before filling. Fill to the UPPER LEVEL as indicated on the battery. Note: Never fill/activate a battery installed in a vehicle as electrolyte spillage can cause damage.
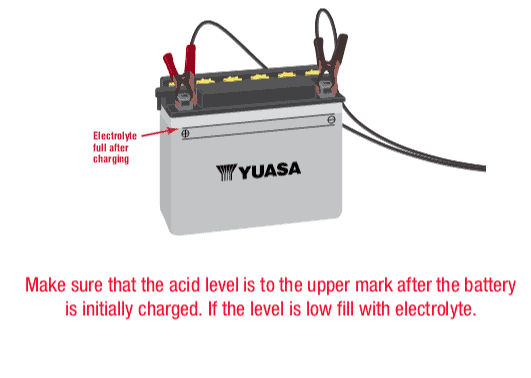
- Fill each battery cell slowly and carefully to the highest level line.
- Let the battery stand for at least 30 minutes after filling. Move or gently tap the battery so that any air bubbles between the plates will be expelled. If the acid level has fallen, refill with acid to the upper level.
- Filling a Conventional battery with electrolyte will bring it to a 75-80% charge. A battery must be charged to 100% before putting it into service. To find recommended charging current requirements in amps for a specific battery, divide the battery ampere-hour capacity rating by 10. For example, a 14 AH battery should be charged at 1.4 amps (14 AH ÷ 10 = 1.4 amps). The specific gravity of the electrolyte should rise to at least 1.260 on 12N series batteries. On all High-Performance batteries (YB Series) a minimal reading of 1.280 should be observed.
- During initial charging, check to see if the electrolyte level has fallen and if so, fill the battery with acid to the UPPER LEVEL. After adding acid, charge for another hour at the same rate as above to mix the water and acid together. Note: This is the last time electrolyte should be added to the battery. If the level is low during use, distilled water should be added as required.
- When charging is complete, replace the filler cap plugs and tighten them by hand – do not use a screwdriver or pliers. Wash off spilled acid with water and baking soda solution, paying particular attention that any acid is washed off the terminals. Dry the battery case and install the battery.
Activating a Conventional battery is a simple process that nearly any rider or mechanic can follow with success. Remember to always practice caution when handling batteries and activation equipment.






